

|
last update 20 Sep 2009 |
|
#include <cvrGenericLattice1D.h>
Public Types | |
Internal types and classes | |
| typedef cvr::constReferenceException | constReferenceException |
| typedef genericVector< T > ::value_type | value_type |
| typedef genericVector< T > ::size_type | size_type |
| typedef genericVector< T >::pointer | pointer |
| typedef genericVector< T > ::const_pointer | const_pointer |
| typedef genericVector< T > ::reference | reference |
| typedef genericVector< T > ::const_reference | const_reference |
| typedef genericVector< T > ::iterator | iterator |
| typedef genericVector< T > ::const_iterator | const_iterator |
Public Member Functions | |
| genericLattice1D () | |
| genericLattice1D (const size_type from, const size_type to) | |
| genericLattice1D (const iinterval &indices) | |
| genericLattice1D (const size_type from, const size_type to, const_reference iniValue) | |
| genericLattice1D (const iinterval &indices, const_reference iniValue) | |
| genericLattice1D (const size_type from, const size_type to, const value_type data[]) | |
| genericLattice1D (const iinterval &indices, const value_type data[]) | |
| genericLattice1D (const size_type from, const size_type to, value_type data[], const eConstantReference constRef) | |
| genericLattice1D (const iinterval &indices, value_type data[], const eConstantReference constRef) | |
| genericLattice1D (const genericLattice1D< T > &other) | |
| genericLattice1D (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, const size_type from, const size_type to=MaxIndex) | |
| genericLattice1D (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, const iinterval &indices) | |
| genericLattice1D (const std::vector< T > &other, const int firstIndex=0) | |
| genericLattice1D (const genericVector< T > &other, const int firstIndex=0) | |
| virtual | ~genericLattice1D () |
| bool | ownsData () const |
| void | restoreOwnership () |
| void | useExternData (const size_type from, const size_type to, pointer data, const eConstantReference constRef=VariableReference) |
| void | useExternData (const iinterval &indices, pointer data, const eConstantReference constRef=VariableReference) |
| void | attach (const size_type from, const size_type to, value_type data[]) |
| void | attach (const iinterval &indices, pointer data) |
| void | detach (genericLattice1D< T > &receiver) |
| void | swap (genericLattice1D< T > &other) |
| size_type | size () const |
| const_iterator | begin () const |
| iterator | begin () |
| size_type | firstIndex () const |
| size_type | lastIndex () const |
| const_iterator | end () const |
| iterator | end () |
| iterator | inverseBegin () |
| const_iterator | inverseBegin () const |
| iterator | inverseEnd () |
| const_iterator | inverseEnd () const |
| void | resize (const size_type from, const size_type to, const_reference iniValue, const eResizeType resizeType=CopyAndInit) |
| void | resize (const iinterval &indices, const_reference iniValue, const eResizeType resizeType=CopyAndInit) |
| void | resize (const size_type from, const size_type to) |
| void | resize (const iinterval &indices) |
| void | allocate (const size_type from, const size_type to) |
| void | allocate (const iinterval &indices) |
| void | assign (const size_type from, const size_type to, const_reference initValue) |
| void | assign (const iinterval &indices, const_reference initValue) |
| void | clear () |
| bool | empty () const |
| void | fill (const_reference iniValue, const size_type from=MinIndex, const size_type to=MaxIndex) |
| void | fill (const_reference iniValue, const iinterval &indices) |
| void | fill (const value_type data[], const size_type from=MinIndex, const size_type to=MaxIndex) |
| void | fill (const value_type data[], const iinterval &indices) |
| void | fill (const genericLattice1D< T > &lat, const size_type from=MinIndex, const size_type to=MaxIndex, const size_type startAt=0) |
| void | fill (const genericLattice1D< T > &vct, const iinterval &indices, const size_type startAt=0) |
| reference | at (const size_type x) |
| const_reference | at (const size_type x) const |
| reference | operator[] (const size_type x) |
| const_reference | operator[] (const size_type x) const |
| reference | elem (const size_type n) |
| const_reference | elem (const size_type n) const |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | copy (const genericLattice1D< T > &other) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | copy (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, const size_type from, const size_type to=MaxIndex) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | copy (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, const iinterval &indices) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | operator= (const genericLattice1D< T > &other) |
| virtual const std::string & | name () const |
| virtual genericLattice1D< T > * | clone () const |
| virtual genericLattice1D< T > * | newInstance () const |
| bool | equals (const genericLattice1D< T > &other) const |
| bool | operator== (const genericLattice1D< T > &other) const |
| bool | operator!= (const genericLattice1D< T > &other) const |
| template<typename U > | |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | castFrom (const genericLattice1D< U > &other) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | castFrom (const genericLattice1D< T > &other) |
| template<typename U > | |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | castFrom (const genericLattice1D< U > &other, const size_type from, const size_type to=MaxIndex) |
| template<typename U > | |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | castFrom (const genericLattice1D< U > &other, const iinterval &indices) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | castFrom (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, const size_type from, const size_type to=MaxIndex) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | castFrom (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, const iinterval &indices) |
| template<typename U > | |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | castFrom (const std::vector< U > &other, const int firstIndex=0) |
| template<typename U > | |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | castFrom (const genericVector< U > &other, const int firstIndex=0) |
| const genericVector< T > & | getAsVector () const |
Apply Methods | |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | apply (T(*function)(T)) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | apply (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, T(*function)(T)) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | apply (T(*function)(const T &)) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | apply (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, T(*function)(const T &)) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | apply (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, T(*function)(const T &, const T &)) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | apply (const genericLattice1D< T > &other, T(*function)(T, T)) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | apply (const genericLattice1D< T > &a, const genericLattice1D< T > &b, T(*function)(const T &, const T &)) |
| genericLattice1D< T > & | apply (const genericLattice1D< T > &a, const genericLattice1D< T > &b, T(*function)(T, T)) |
Input and Output | |
| virtual bool | write (ioHandler &handler, const bool complete=true) const |
| virtual bool | read (ioHandler &handler, const bool complete=true) |
Protected Attributes | |
| size_type | first_ |
| size_type | last_ |
| pointer | theElements0_ |
| genericVector< T > | data_ |
This container is inspired on mathematical integer lattices, at least with respect to the indices, which are taken from 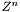 in the general case with $n=1$ in this particular case.
in the general case with $n=1$ in this particular case.
You can consider this a generalization of a cvr::genericVector, in which the index of the first element is not necessarily zero, but a negative or positive value.
The main goal of this class is to provide a fast implementation for random access containers, addressable with negative indices, like filter kernels, and since speed is the premise, it is achieved at some memory costs. This means this class has some storage overhead in order to provide some information at zero time, like size, first and last indices the begin and end iterators, etc., which is only possible by storing them directly.
This class cannot be used to contain objects which use some sort of dynamic memory allocation. This means, you should not try to make a cvr::genericLattice1D of other vectors or matrices, which administrate some memory. If you do so, the behaviour of copy or fill operations will be unpredictable.
Most of times you will want to use cvr::lattice1D instead, since they provide some mathematical functionality.
The difference between cvr::genericLattice1D and its most used inherited class cvr::lattice1D is the support for arithmetical operations. The generic lattice is more a "pure" container. It inherits its memory management versatility to cvr::lattice1D. Again, it is usually employed as a container of any static type, which do not do by itself any memory managment.
The genericLattice1D class is a generic container class implemented as a template, where the template type T is the type of the elements assigned to each point in the lattice.
If you need to create a lattice of floats with 255 elements indexed from -127 to 127, all of them initialized with a value of 4.27 just create it with
cvr::genericLattice1D<float> myLat(-127,127,4.27f);
To access the lattice elements use the access operators at() (or the overloaded operator[]()). For example:
float accu = 0; // initialize accumulator for (int i = myLat.firstIndex(); i <= myLat.lastIndex(); i++) { accu += myLat.at(i); // access each element of the vector }
In the CVR-Lib, the debug-mode library always makes a boundary check for both at() and operator[](), and in the release-mode there is no check for any of both methods.
| typedef genericVector<T>::const_iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::const_iterator |
const_iterator type (allows read-only operations).
The use of the iterator classes is similar to the iterators of the STL (Standard Template Library). See cvr::genericLattice1D::begin() for an example.
For the debugging version of the iterators, boundary check will be done! This explains the low speed of the iterators of the debug version. In the release version, no boundary check will be done, and the iterators are sometimes a factor 10 faster than the debug iterators.
The use of the access operator at() is faster than the iterators in the debug version only. If you need to iterate on a genericLattice1D use iterators instead (in the release version iterators are approximately a factor 3 faster than at()).
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| typedef genericVector<T>::const_pointer cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::const_pointer |
Const pointer to value_type.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| typedef genericVector<T>::const_reference cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::const_reference |
Const reference to value_type.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| typedef cvr::constReferenceException cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::constReferenceException |
Exception thrown when a constant reference is violated.
Reimplemented in cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| typedef genericVector<T>::iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::iterator |
iterator type (allows read and write operations).
The use of the iterator classes is similar to the iterators of the STL (Standard Template Library). See cvr::genericLattice1D::begin() and cvr::genericLattice1D::inverseBegin() for examples.
For the debugging version of the iterators, boundary check will be done! This explains the low speed of the iterators of the debug version. In the release version, no boundary check will be done, and the iterators are sometimes a factor 10 faster than the debug iterators.
The use of the access operator at() is faster than the iterators in the debug version only. If you need to iterate on a genericLattice1D use iterators instead (in the release version iterators are approximately a factor 3 faster than at()).
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| typedef genericVector<T>::pointer cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::pointer |
Pointer to value_type.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| typedef genericVector<T>::reference cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::reference |
Reference to value_type.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| typedef genericVector<T>::size_type cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::size_type |
Return type of the size() member.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| typedef genericVector<T>::value_type cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::value_type |
Type of the genericLattice1D elements.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | ) |
Default constructor creates an empty genericLattice1D.
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to | |||
| ) | [explicit] |
Create a genericLattice1D indexed by the given interval but do not initialize its elements.
| from | initial index. | |
| to | final index. |
to value must be greater or equal than the from value, otherwise an empty lattice will be created.
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const iinterval & | indices | ) | [explicit] |
Create a genericLattice1D indexed by the given interval but do not initialize its elements.
| indices | interval of indices to be used. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to, | |||
| const_reference | iniValue | |||
| ) | [explicit] |
Create a genericLattice1D indexed by the given interval and initialize it with the given value.
| from | initial index value | |
| to | final index value | |
| iniValue | all elements will be initialized with this value. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const iinterval & | indices, | |
| const_reference | iniValue | |||
| ) | [explicit] |
Create a genericLattice1D indexed by the given interval and initialize it with the given value.
| indices | interval of indices to be used. | |
| iniValue | all elements will be initialized with this value. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to, | |||
| const value_type | data[] | |||
| ) |
Create a genericLattice1D indexed by the given interval and initialize it with the given data.
The data will be copied.
If you need to just use the memory block without copying it, then you can wether use a third parameter of eConstantReference type or later call the useExternData() method.
| from | initial index value | |
| to | final index value | |
| data | a pointer to the data that will be copied. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const iinterval & | indices, | |
| const value_type | data[] | |||
| ) |
Create a genericLattice1D indexed by the given interval and initialize it with the given data.
The data will be copied.
If you need to just use the memory block without copying it, then you can wether use a third parameter of eConstantReference type or later call the useExternData() method.
| indices | interval of indices to be used. | |
| data | a pointer to the data that will be copied. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to, | |||
| value_type | data[], | |||
| const eConstantReference | constRef | |||
| ) |
Create a genericLattice1D indexed by the given interval and initialize it with the given data, the same way "useExternData" does, i.e.
the data will not be copied!.
| from | initial index | |
| to | final index | |
| data | a pointer to the data that will be used. | |
| constRef | if this parameter is ConstantReference it will not be possible to change the pointer to the external memory block nor to resize the genericLattice1D. Despite this, the value of each element can be changed by the access operators. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const iinterval & | indices, | |
| value_type | data[], | |||
| const eConstantReference | constRef | |||
| ) |
Create a genericLattice1D indexed by the given interval and initialize it with the given data, the same way "useExternData" does, i.e.
the data will not be copied!.
| indices | interval used for the lattice indices | |
| data | a pointer to the data that will be used. | |
| constRef | if this parameter is ConstantReference it will not be possible to change the pointer to the external memory block nor to resize the genericLattice1D. Despite this, the value of each element can be changed by the access operators. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other | ) |
Create this genericLattice1D as a copy of another genericLattice1D.
| other | the genericLattice1D to be copied. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| const size_type | from, | |||
| const size_type | to = MaxIndex | |||
| ) |
Create this genericLattice1D as a copy of the specified interval of elements of another genericLattice1D.
The from and to values are truncated to the interval used by the other lattice.
| other | the genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| from | starting index of other lattice. | |
| to | end index of the other lattice. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| const iinterval & | indices | |||
| ) |
Create this genericLattice1D as a copy of the specified interval of elements of another genericLattice1D.
The from and to values are truncated to the interval used by the other lattice.
| other | the genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| indices | index interval of the elements of other to be copied. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const std::vector< T > & | other, | |
| const int | firstIndex = 0 | |||
| ) |
Create this genericLattice1D as a copy of another std::vector<T>.
| other | the genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| firstIndex | index to be used for the first element of the vector. |
| cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::genericLattice1D | ( | const genericVector< T > & | other, | |
| const int | firstIndex = 0 | |||
| ) |
Create this genericLattice1D as a copy of another cvr::genericVector.
| other | the genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| firstIndex | optional argument indicating which index is going to be assigned to the first vector element. |
| virtual cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::~genericLattice1D | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Destructor.
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::allocate | ( | const iinterval & | indices | ) | [inline] |
Change the vector to contain exactltly the given number of elements.
In opposition to resize, allocate() does not copy the previous data but only modifies the size of the vector, discarding all contained data and leaving the new data uninitialized.
This is in principle an alias to resize(newSize,T(),AllocateOnly).
| indices | interval used for the indices of this lattice. |
resize(const int,const int,const_reference, const eResizeType)
resize(const int),allocate(), assign()
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::allocate | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Change the vector to contain exactltly the given number of elements.
In opposition to resize, allocate() does not copy the previous data but only modifies the size of the vector, discarding all contained data and leaving the new data uninitialized.
This is in principle an alias to resize(newSize,T(),AllocateOnly).
| from | initial index | |
| to | final index |
resize(const int),allocate(), assign()
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::apply | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | a, | |
| const genericLattice1D< T > & | b, | |||
| T(*)(T, T) | function | |||
| ) |
A two-parameter C-function receives the i-th elements of the given genericLattice1Ds and leaves the result here.
Note that both genericLattice1Ds MUST have the same size! If both genericLattice1Ds have different size, the function will throw an assertion without changing anything!
| a | the first genericLattice1D | |
| b | the second genericLattice1D | |
| function | a pointer to a two parameters C-function |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::apply | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | a, | |
| const genericLattice1D< T > & | b, | |||
| T(*)(const T &, const T &) | function | |||
| ) |
A two-parameter C-function receives the i-th elements of the given genericLattice1Ds and leaves the result here.
Note that both genericLattice1Ds MUST have the same size! If both genericLattice1Ds have different size, the function will throw an assertion without changing anything!
The following example uses cvr::min as function. The genericLattice1Ds a and b contain the values [1,2,3,4] and [4,3,2,1], respectively. After applying the function, genericLattice1D c contains the values [1,2,2,1].
igenericLattice1D a,b,c; int i=0; for (i=0; i<4; ++i) { a.at(i)=i+1; b.at(i)=4-i; } c.apply(a,b,cvr::min);
| a | the first genericLattice1D | |
| b | the second genericLattice1D | |
| function | a pointer to a two parameters C-function |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::apply | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| T(*)(T, T) | function | |||
| ) |
A two-parameter C-function receives the i-th elements of this and the given genericLattice1D and the result will be left in this genericLattice1D.
Note that both genericLattice1Ds MUST have the same size! If both genericLattice1Ds have different size, the function will throw an assertion without changing anything!
| other | the second genericLattice1D to be considered (the first genericLattice1D will be this object!) | |
| function | a pointer to a two parameters C-function |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::apply | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| T(*)(const T &, const T &) | function | |||
| ) |
A two-parameter C-function receives the i-th elements of this and the given genericLattice1D and the result will be left in this genericLattice1D.
Note that both genericLattice1Ds MUST have the same size! If both genericLattice1Ds have different size, the function will throw an assertion without changing anything!
| other | the second genericLattice1D to be considered (the first genericLattice1D will be this object!) | |
| function | a pointer to a two parameters C-function |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::apply | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| T(*)(const T &) | function | |||
| ) |
Applies a C-function to each element the other genericLattice1D and leaves the result here.
| other | the genericLattice1D with the source data | |
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::apply | ( | T(*)(const T &) | function | ) |
Applies a C-function to each element of the genericLattice1D.
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::apply | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| T(*)(T) | function | |||
| ) |
Applies a C-function to each element of the other genericLattice1D and leaves the result here.
| other | the source genericLattice1D | |
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::apply | ( | T(*)(T) | function | ) |
Applies a C-function to each element of the genericLattice1D.
In the following example, genericLattice1D vct is initialized with 4.0. After applying sqrt(), all elements of vct are 2.0.
genericLattice1D<float> vct(4,4.0); vct.apply(sqrt);
| function | a pointer to a C-function |
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::assign | ( | const iinterval & | indices, | |
| const_reference | initValue | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Assign copies of initValue to the genericVector such that the given interval is covered.
Change the size and contents of this vector to be exactly newSize elements long, with all the elements initialized to the value indicated in initValue. In opposition to resize, this method does not copy the previous data but changes the size of the vector, discarding all contained data, replacing it with newSize copies of initValue.
This is in principle an alias to resize(newSize,T(),Init).
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::assign | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to, | |||
| const_reference | initValue | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Assign copies of initValue to the genericVector such that the given interval is covered.
Change the size and contents of this vector to be exactly newSize elements long, with all the elements initialized to the value indicated in initValue. In opposition to resize, this method does not copy the previous data but changes the size of the vector, discarding all contained data, replacing it with newSize copies of initValue.
This is in principle an alias to resize(newSize,T(),Init).
| from | initial index. | |
| to | final index. | |
| initValue | all elements of the vector will be initialized with this value. |
| const_reference cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::at | ( | const size_type | x | ) | const [inline] |
Access element x of the genericLattice1D in a read-only modus.
| x | index of the genericLattice1D element to be accessed. It should be between firstIndex() and lastIndex() |
| reference cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::at | ( | const size_type | x | ) | [inline] |
Access element x of the genericLattice1D.
| x | index of the genericLattice1D element to be accessed. It should be between firstIndex() and lastIndex() |
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::attach | ( | const iinterval & | indices, | |
| pointer | data | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Attach extern data to the vector.
This member allows the use of this object as an access-functor for the 'data'. An access to the element at(x) is equivalent to data[x]. If theSize is an invalid dimension, the behaviour will be unpredictible.
The memory will be administrated by this genericLattice1D instance, and may be deleted if required (e.g. genericLattice1D deleted or resized!). The user should not try to manipulate the memory allocation of the data after the attachment! See also useExternData().
| indices | interval of indices for the lattice. | |
| data | a pointer to the memory block to be used |
cvr::genericLattice1D<int> myLat; int block1[25]; int* block2; block2 = new int[25]; myLat.useExternData(25,block1); // ok myLat.attach(25,block1); // wrong!!! matrix will try to manipulate // stack memory: DO NOT DO THIS!!!!! myLat.attach(25,block2); // ok! but do not try to delete the memory // block2!!
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::attach | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to, | |||
| value_type | data[] | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Attach extern data to the vector.
This member allows the use of this object as an access-functor for the 'data'. An access to the element at(x) is equivalent to data[x]. If theSize is an invalid dimension, the behaviour will be unpredictible.
The memory will be administrated by this genericLattice1D instance, and may be deleted if required (e.g. genericLattice1D deleted or resized!). The user should not try to manipulate the memory allocation of the data after the attachment! See also useExternData().
| from | initial index | |
| to | final index | |
| data | a pointer to the memory block to be used |
cvr::genericLattice1D<int> myLat; int block1[25]; int* block2; block2 = new int[25]; myLat.useExternData(25,block1); // ok myLat.attach(25,block1); // wrong!!! matrix will try to manipulate // stack memory: DO NOT DO THIS!!!!! myLat.attach(25,block2); // ok! but do not try to delete the memory // block2!!
| iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::begin | ( | ) | [inline] |
Returns iterator pointing to the first element.
The use of the iterators is similar to the iterators of the Standard Template Library (STL). If you need to iterate on all elements of the genericLattice1D, you can use following code:
int tmp,accu; // a temporal variable // genericLattice1D with 10 elements cvr::genericLattice1D<int> myLat(10,1); // an iterator set to the beginning of myLat cvr::genericLattice1D<int>::iterator it=myLat.begin(); // an iterator set to the end of myLat cvr::genericLattice1D<int>::iterator eit=myLat.begin(); for (; it!=eit ; ++it) { tmp = *it; // tmp has value of element pointed // by the iterator. accu += tmp; (*it) = accu; // change the value in the genericLattice1D. }
| const_iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::begin | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns first element as a const_iterator.
Note that you can not change the values of the genericLattice1D elements when you use a const_iterator. See also begin()
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::castFrom | ( | const genericVector< U > & | other, | |
| const int | firstIndex = 0 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::castFrom | ( | const std::vector< U > & | other, | |
| const int | firstIndex = 0 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::castFrom | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| const iinterval & | indices | |||
| ) |
This is just an alias for copy(const genericLattice1D<T>&, const size_type from, const size_type to) to facilitate generic programming.
| other | The genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| indices | interval of other to be copied in this lattice. |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::castFrom | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| const size_type | from, | |||
| const size_type | to = MaxIndex | |||
| ) |
This is just an alias for copy(const genericLattice1D<T>&, const size_type from, const size_type to) to facilitate generic programming.
| other | The genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| from | starting point included | |
| to | end point included |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::castFrom | ( | const genericLattice1D< U > & | other, | |
| const iinterval & | indices | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Copy a subvector of the other genericLattice1D by casting each of its elements.
| other | The genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| indices | interval of indices to be copied from other. |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::castFrom | ( | const genericLattice1D< U > & | other, | |
| const size_type | from, | |||
| const size_type | to = MaxIndex | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Copy a subvector of the other genericLattice1D by casting each of its elements.
| other | The genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| from | starting point included | |
| to | end point included. |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::castFrom | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other | ) |
This is just an alias for copy(const genericLattice1D<T>&) to facilitate generic programming.
| other | The genericLattice1D to be copied. |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::castFrom | ( | const genericLattice1D< U > & | other | ) | [inline] |
Copy the other genericLattice1D by casting each of its elements.
| other | The genericLattice1D to be copied. |
cvr::genericLattice1D<int> vctA(10,1);// a genericLattice1D of ints cvr::genericLattice1D<double> vctB; // a genericLattice1D of doubles vctB.castFrom(vctA); // this will copy vctA in vctB!!
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::clear | ( | ) |
Removes all elements from the genericVector (Set dimensions to 0).
| virtual genericLattice1D<T>* cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::clone | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Create a clone of this genericLattice1D.
Implements cvr::container.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::copy | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| const iinterval & | indices | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Assignment operator.
Copy a specified interval of elements of another genericLattice1D. At the end this vector will contain t-f+1 elements, where f=max(0,from) and t=min(other.lastIndex()-1,to).
| other | the genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| indices | interval of the other lattice to be copied into this one. |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::copy | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other, | |
| const size_type | from, | |||
| const size_type | to = MaxIndex | |||
| ) |
Assignment operator.
Copy a specified interval of elements of another genericLattice1D. At the end this vector will contain t-f+1 elements, where f=max(other.firstIndex(),from) and t=min(other.lastIndex(),to).
| other | the genericLattice1D to be copied. | |
| from | starting index | |
| to | final index. |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::copy | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other | ) |
Assigment operator.
Copy the contents of other in this object.
If this instance has a constReference, then only the contents are copied.
| other | the source genericLattice1D to be copied. |
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::detach | ( | genericLattice1D< T > & | receiver | ) |
Free the data of this object and hand it over to the "receiver".
The value of ownsData is also transfered to the receiver. (see Note).
This function makes a "memory block transfusion" to another genericLattice1D. It is a very efficient way to make a copy of this genericLattice1D, if you don't need the source data anymore!
Note: Take care that if the attach() or useExternData() methods of this genericLattice1D have been called before detachment, the same rules for memory management apply now for the receiver.
At the end of the detachment, this genericLattice1D will be empty.
| receiver | the genericLattice1D which will receive the memory block. All data of that genericLattice1D will be first deleted! |
| const_reference cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::elem | ( | const size_type | n | ) | const [inline] |
Constant access to element n of the genericLattice1D as a vector.
The lattice is indexed from 0 to to-from.
This member function is needed for generic programming with different container types.
| reference cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::elem | ( | const size_type | n | ) | [inline] |
Access element n of the genericLattice1D as a vector.
The lattice is indexed from 0 to to-from.
This member function is needed for generic programming with different container types.
| bool cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::empty | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns true if the genericVector is empty.
| iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::end | ( | ) | [inline] |
Returns last index as an iterator.
For an example see begin()
| const_iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::end | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns last index as a const_iterator.
For an example see begin()
| bool cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::equals | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other | ) | const |
Compare this genericLattice1D with other.
| other | the other genericLattice1D to be compared with |
true if both genericLattice1Ds have the same elements and same definition interval | void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::fill | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | vct, | |
| const iinterval & | indices, | |||
| const size_type | startAt = 0 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Fills the genericLattice1D elements from from to to with the elements of vct starting at startAt.
| vct | genericLattice1D with the elements to be copied. | |
| indices | interval of the lattice to be filled. | |
| startAt | start index of the source genericLattice1D vct. |
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::fill | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | lat, | |
| const size_type | from = MinIndex, |
|||
| const size_type | to = MaxIndex, |
|||
| const size_type | startAt = 0 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Fills the genericLattice1D elements from from to to with the elements of vct starting at startAt.
| lat | genericLattice1D with the elements to be copied | |
| from | first element index of the actual genericLattice1D | |
| to | last element index of the actual genericLattice1D | |
| startAt | start index of the source genericLattice1D vct. |
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::fill | ( | const value_type | data[], | |
| const iinterval & | indices | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Fills the genericLattice1D elements with data pointed by data between from and to.
| data | the data to by copied into this genericLattice1D | |
| indices | interval of the lattice to be filled in. |
Example:
double* data = {2,4,8,16}; cvr::genericLattice1D<double> myLat(-5,5,0);// genericLattice1D with // 11 elements with 0 myLat.fill(data,1,3); // myLat=[0,0,0,0,0,0,2,4,8,0,0]
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::fill | ( | const value_type | data[], | |
| const size_type | from = MinIndex, |
|||
| const size_type | to = MaxIndex | |||
| ) |
Fills the genericLattice1D elements with data pointed by data between from and to.
| data | the data to by copied into this genericLattice1D | |
| from | first element index | |
| to | last element index |
Example:
double* data = {2,4,8,16}; cvr::genericLattice1D<double> myLat(10,0);// genericLattice1D with 10 // elements with 0 myLat.fill(data,1,3); // myLat=[0,2,4,8,0,0,0,0,0,0]
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::fill | ( | const_reference | iniValue, | |
| const iinterval & | indices | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Fills the genericLattice1D elements with iniValue between from and to.
| iniValue | the elements will be initialized with this value. | |
| indices | interval of the lattice to be filled in |
Example:
cvr::genericLattice1D<double> myLat(0,9,0); // genericLattice1D with // 10 elements with 0 myLat.fill(9,iinterval(1,3)); // myLat=[0,9,9,9,0,0,0,0,0,0]
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::fill | ( | const_reference | iniValue, | |
| const size_type | from = MinIndex, |
|||
| const size_type | to = MaxIndex | |||
| ) |
Fills the genericLattice1D elements with iniValue between from and to.
| iniValue | the elements will be initialized with this value. | |
| from | first element index | |
| to | last element index |
Example:
cvr::genericLattice1D<double> myLat(-1,8,0); // genericLattice1D with // 10 elements with 0 myLat.fill(9,1,3); // myLat=[0,0,9,9,9,0,0,0,0,0]
| size_type cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::firstIndex | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns first index (in a genericLattice1D this is always size()-1).
| const genericVector<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::getAsVector | ( | ) | const [inline] |
| const_iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::inverseBegin | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Return an iterator that points to the last valid element of the genericLattice1D.
See inverseBegin() for more details.
| iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::inverseBegin | ( | ) | [inline] |
This method returns an iterator that points to the last valid element of the genericLattice1D.
It is used for inverse order iteration through the genericLattice1D using normal iterators (as opposed to reverse_iterators used in the STL). This has the advantage that iterators going from front to end and in the inverse direction are the same and can thus be compared, copied etc. Further the implementation of reverse_iterators is not as fast as that of iterators and thus not desired in the CVR-Lib.
igenericLattice1D v(false,10); int i,tmp; for (i=0; i<10; i++) { v.at(i)=i; } igenericLattice1D::iterator forwardIt=v.begin(); igenericLattice1D::iterator backIt=v.inverseBegin(); while (forwardIt<=backIt) { tmp = (*forwardIt); (*forwardIt)=(*backIt); (*backIt)=tmp; ++forwardIt; ++backIt; }
| const_iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::inverseEnd | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Return an iterator that points to the element before the first valid element of the genericLattice1D.
| iterator cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::inverseEnd | ( | ) | [inline] |
Return an iterator that points to the element before the first valid element of the genericLattice1D.
It is used to mark the end for inverse order iteration through the genericLattice1D using normal iterators (as opposed to reverse_iterators as used in the STL). This has the advantage that iterators going from front to end and in the inverse direction are the same and can thus be compared, copied etc.Further the implementation of reverse_iterators is not as fast as that of iterators and thus not desired in the CVR-Lib.
| size_type cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::lastIndex | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns last index (in a genericLattice1D this is always size()-1).
| virtual const std::string& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::name | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Returns the name of this type.
Implements cvr::ioObject.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| virtual genericLattice1D<T>* cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::newInstance | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Create a clone of this genericLattice1D.
Implements cvr::container.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, cvr::lattice1D< T >, and cvr::lattice1D< int >.
| bool cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::operator!= | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other | ) | const [inline] |
Compare this genericLattice1D with other.
| other | the other genericLattice1D to be compared with. |
| genericLattice1D<T>& cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::operator= | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other | ) |
Assigment operator (alias for copy(other)).
| other | the genericLattice1D to be copied |
| bool cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::operator== | ( | const genericLattice1D< T > & | other | ) | const [inline] |
Compare this genericLattice1D with other.
| other | the other genericLattice1D to be compared with |
| const_reference cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::operator[] | ( | const size_type | x | ) | const [inline] |
Constant access operator (alias for at(const size_type x) const).
| reference cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::operator[] | ( | const size_type | x | ) | [inline] |
Access operator (alias for at(const size_type x)).
| bool cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::ownsData | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Check whether this object owns the data.
| virtual bool cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::read | ( | ioHandler & | handler, | |
| const bool | complete = true | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
Read the object from the given ioHandler.
Reimplemented from cvr::ioObject.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >.
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::resize | ( | const iinterval & | indices | ) | [inline] |
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::resize | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Resize the vector keeping all the old elements, but without initializing the new ones.
This is an alias for resize(from,to,T(),Copy);
| from | initial index | |
| to | final index |
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::resize | ( | const iinterval & | indices, | |
| const_reference | iniValue, | |||
| const eResizeType | resizeType = CopyAndInit | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Change dimension and if desired the contents of the genericVector.
| indices | interval to be used by the lattice indices. | |
| iniValue | the initialization value. | |
| resizeType | specifies what should happen with the data of the resized vector. |
cvr::genericVector<int> myVct; // creates empty genericVector myVct.resize(5,0); // genericVector with 5 elements initialized // with 0 myVct.resize(10,2); // genericVector has now 10 elements: the // first five are still 0 and the // rest have a 2 myVct.resize(20,3,cvr::AllocateOnly); // now the genericVector has 20 // elements but their values // are unknown. myVct.resize(5,1,cvr::Init); // the genericVector has now 5 // elements initialized with 1
If the resize is possible (see useExternData()), after the resize, this object will always own the data!
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::resize | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to, | |||
| const_reference | iniValue, | |||
| const eResizeType | resizeType = CopyAndInit | |||
| ) |
Change dimension and if desired the contents of the genericVector.
| from | initial index | |
| to | final index | |
| iniValue | the initialization value. | |
| resizeType | specifies what should happen with the data of the resized vector. |
cvr::genericVector<int> myVct; // creates empty genericVector myVct.resize(5,0); // genericVector with 5 elements initialized // with 0 myVct.resize(10,2); // genericVector has now 10 elements: the // first five are still 0 and the // rest have a 2 myVct.resize(20,3,cvr::AllocateOnly); // now the genericVector has 20 // elements but their values // are unknown. myVct.resize(5,1,cvr::Init); // the genericVector has now 5 // elements initialized with 1
If the resize is possible (see useExternData()), after the resize, this object will always own the data!
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::restoreOwnership | ( | ) | [inline] |
Restore ownership.
If this object does not own its data, this member will create a new memory buffer with the same data and will make this vector its owner.
If this genericLattice1D already owns its data nothing happens.
| size_type cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::size | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the number of elements of the genericLattice1D.
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::swap | ( | genericLattice1D< T > & | other | ) |
Exchange (in a fast way) the data between this and the other genericLattice1D.
Similar to detach(), this method will exchange the complete memory blocks, avoiding an element-wise copy.
| other | the genericLattice1D with which the data will be exchanged. |
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::useExternData | ( | const iinterval & | indices, | |
| pointer | data, | |||
| const eConstantReference | constRef = VariableReference | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Reference to extern data.
This member allows the use of this object as an wrapper-object to access some memory block as a genericLattice1D. The user must take care for memory allocation and deallocation of the block. This object will never delete the external data!.
| indices | interval to be used by the lattice to access the data. Note that this is NOT the number of bytes of the external block. | |
| data | pointer to the external memory block. | |
| constRef | if this parameter is true, it will not be possible to change the pointer to the external memory block nor to resize the genericLattice1D. Despite this, the value of each element can be changed by the access operators. |
int i; double tmp; double a[10]; // memory block! for (i=0;i<10;i++) { a[i]=2*i; // initialize the memory block } cvr::genericLattice1D<double> myLat; // an empty genericLattice1D myLat.resize(-2,2,0); // resize the genericLattice1D: now 5 // elements initialized with 0 myLat.useExternData(-4,5,a,true); // use the genericLattice1D as wrapper // for the memory block tmp = myLat.at(5); // tmp is now 10 myLat.at(9) = 3; // the last element of myLat // has now the value 3 myLat.resize(0,5); // INVALID!! this will throw an exception // constReferenceException()
If the size (from-to+1) is greater than the allocated memory, the behaviour could be unpredictible.
| void cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::useExternData | ( | const size_type | from, | |
| const size_type | to, | |||
| pointer | data, | |||
| const eConstantReference | constRef = VariableReference | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Reference to extern data.
This member allows the use of this object as an wrapper-object to access some memory block as a genericLattice1D. The user must take care for memory allocation and deallocation of the block. This object will never delete the external data!.
| from | initial index | |
| to | final index | |
| data | pointer to the external memory block. | |
| constRef | if this parameter is true, it will not be possible to change the pointer to the external memory block nor to resize the genericLattice1D. Despite this, the value of each element can be changed by the access operators. |
int i; double tmp; double a[10]; // memory block! for (i=0;i<10;i++) { a[i]=2*i; // initialize the memory block } cvr::genericLattice1D<double> myLat; // an empty genericLattice1D myLat.resize(-2,2,0); // resize the genericLattice1D: now 5 // elements initialized with 0 myLat.useExternData(-4,5,a,true); // use the genericLattice1D as wrapper // for the memory block tmp = myLat.at(5); // tmp is now 10 myLat.at(9) = 3; // the last element of myLat // has now the value 3 myLat.resize(0,5); // INVALID!! this will throw an exception // constReferenceException()
If the size (from-to+1) is greater than the allocated memory, the behaviour could be unpredictible.
| virtual bool cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::write | ( | ioHandler & | handler, | |
| const bool | complete = true | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Write the object in the given ioHandler.
Reimplemented from cvr::ioObject.
Reimplemented in cvr::kernel1D< T >.
genericVector<T> cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::data_ [protected] |
A generic vector is used to contain the data.
size_type cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::first_ [protected] |
Index of the last element of the genericLattice1D.
We sacrifice this sizeof(int) to improve speed in many operations that require this first index.
size_type cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::last_ [protected] |
Index of the last element of the genericLattice1D (always vectorSize-1).
We sacrifice this sizeof(int) to improve speed in many operations that require this last index.
pointer cvr::genericLattice1D< T >::theElements0_ [protected] |
Pointer to the element with index zero.